Kann 0Gs dezentrales KI-Betriebssystem KI wirklich im großen Maßstab On-Chain betreiben?
Am 13. November 2024 gab 0G Labs eine 40 Millionen US-Dollar Finanzierungsrunde bekannt, die von Hack VC, Delphi Digital, OKX Ventures, Samsung Next und Animoca Brands angeführt wurde und das Team hinter diesem dezentralen KI-Betriebssystem ins Rampenlicht rückte. Ihr modularer Ansatz kombiniert dezentralen Speicher, Datenverfügbarkeitsprüfung und dezentrale Abwicklung, um KI-Anwendungen On-Chain zu ermöglichen. Aber können sie realistisch einen Durchsatz von GB/s erreichen, um die nächste Ära der KI-Adoption im Web3 voranzutreiben? Dieser ausführliche Bericht bewertet die Architektur, die Anreizmechanismen, die Ökosystem-Traktion und die potenziellen Fallstricke von 0G, um Ihnen zu helfen, einzuschätzen, ob 0G sein Versprechen halten kann.
Hintergrund
Der KI-Sektor hat einen kometenhaften Aufstieg erlebt, katalysiert durch große Sprachmodelle wie ChatGPT und ERNIE Bot. Doch KI ist mehr als nur Chatbots und generative Texte; sie umfasst auch alles von AlphaGos Go-Siegen bis hin zu Bildgenerierungstools wie MidJourney. Der Heilige Gral, den viele Entwickler verfolgen, ist eine allgemeine Künstliche Intelligenz oder AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) – umgangssprachlich als KI-„Agent“ beschrieben, der in der Lage ist, zu lernen, wahrzunehmen, Entscheidungen zu treffen und komplexe Ausführungen ähnlich der menschlichen Intelligenz durchzuführen.
Sowohl KI- als auch KI-Agenten-Anwendungen sind jedoch extrem datenintensiv. Sie verlassen sich auf massive Datensätze für Training und Inferenz. Traditionell werden diese Daten auf zentralisierten Infrastrukturen gespeichert und verarbeitet. Mit dem Aufkommen der Blockchain ist ein neuer Ansatz, bekannt als DeAI (Dezentrale KI), entstanden. DeAI versucht, dezentrale Netzwerke für Datenspeicherung, -freigabe und -verifizierung zu nutzen, um die Fallstricke traditioneller, zentralisierter KI-Lösungen zu überwinden.
0G Labs sticht in dieser DeAI-Infrastrukturlandschaft hervor und zielt darauf ab, ein dezentrales KI-Betriebssystem zu entwickeln, das einfach als 0G bekannt ist.
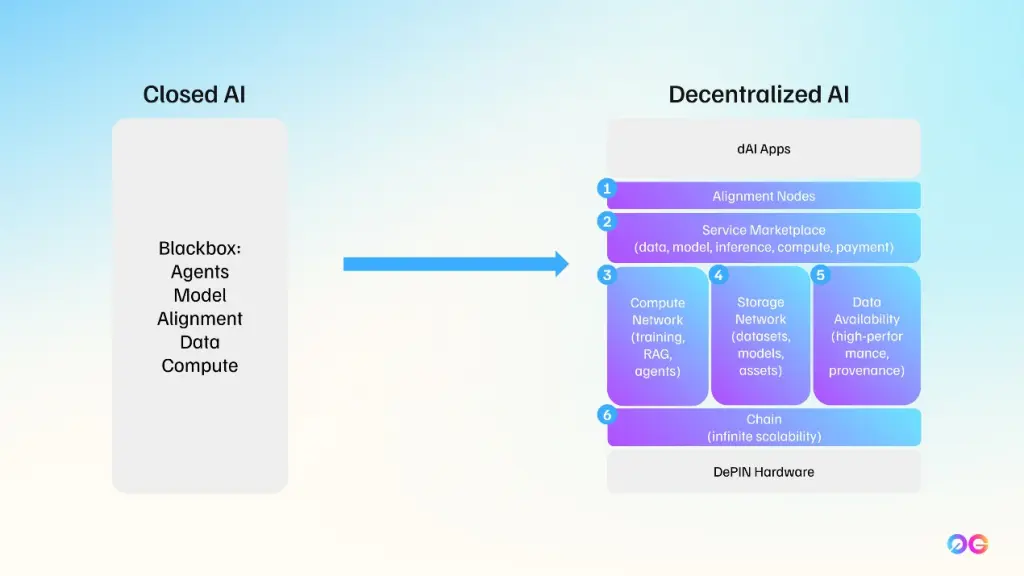
Was ist 0G Labs?
In der traditionellen Informatik verwaltet ein Betriebssystem (OS) Hardware- und Software-Ressourcen – denken Sie an Microsoft Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS oder Android. Ein OS abstrahiert die Komplexität der zugrunde liegenden Hardware und erleichtert sowohl Endbenutzern als auch Entwicklern die Interaktion mit dem Computer.
Analog dazu strebt das 0G OS eine ähnliche Rolle im Web3 an:
- Verwaltung von dezentralem Speicher, Rechenleistung und Datenverfügbarkeit.
- Vereinfachung der Bereitstellung von On-Chain-KI-Anwendungen.
Warum Dezentralisierung? Konventionelle KI-Systeme speichern und verarbeiten Daten in zentralisierten Silos, was Bedenken hinsichtlich Datentransparenz, Benutzerdatenschutz und fairer Vergütung für Datenanbieter aufwirft. Der Ansatz von 0G nutzt dezentralen Speicher, kryptografische Beweise und offene Anreizmodelle, um diese Risiken zu mindern.
Der Name „0G“ steht für „Zero Gravity“ (Schwerelosigkeit). Das Team stellt sich eine Umgebung vor, in der Datenaustausch und Berechnung „schwerelos“ wirken – alles, vom KI-Training über die Inferenz bis zur Datenverfügbarkeit, geschieht nahtlos On-Chain.
Die 0G Foundation, die im Oktober 2024 formell gegründet wurde, treibt diese Initiative voran. Ihre erklärte Mission ist es, KI zu einem öffentlichen Gut zu machen – zugänglich, überprüfbar und offen für alle.

Schlüsselkomponenten des 0G-Betriebssystems
Grundsätzlich ist 0G eine modulare Architektur, die speziell zur Unterstützung von KI-Anwendungen On-Chain entwickelt wurde. Ihre drei Hauptpfeiler sind:
- 0G Storage – Ein dezentrales Speichernetzwerk.
- 0G DA (Data Availability) – Eine spezialisierte Datenverfügbarkeitsschicht, die Datenintegrität gewährleistet.
- 0G Compute Network – Dezentrales Management von Rechenressourcen und Abwicklung für KI-Inferenz (und schließlich Training).
Diese Pfeiler arbeiten unter dem Dach eines Layer1-Netzwerks namens 0G Chain zusammen, das für Konsens und Abwicklung verantwortlich ist.
Gemäß dem 0G Whitepaper („0G: Towards Data Availability 2.0“) bauen sowohl die 0G Storage- als auch die 0G DA-Schicht auf der 0G Chain auf. Entwickler können mehrere benutzerdefinierte PoS-Konsensnetzwerke starten, die jeweils als Teil des 0G DA- und 0G Storage-Frameworks fungieren. Dieser modulare Ansatz bedeutet, dass 0G bei wachsender Systemlast dynamisch neue Validatoren-Sets oder spezialisierte Knoten hinzufügen kann, um zu skalieren.
0G Storage
0G Storage ist ein dezentrales Speichersystem, das für große Datenmengen ausgelegt ist. Es verwendet verteilte Knoten mit integrierten Anreizen für die Speicherung von Benutzerdaten. Entscheidend ist, dass es Daten mithilfe von Erasure Coding (EC) in kleinere, redundante „Chunks“ aufteilt und diese Chunks über verschiedene Speicherknoten verteilt. Wenn ein Knoten ausfällt, können die Daten immer noch aus redundanten Chunks rekonstruiert werden.
Unterstützte Datentypen
0G Storage unterstützt sowohl strukturierte als auch unstrukturierte Daten.
- Strukturierte Daten werden in einer Key-Value (KV)-Schicht gespeichert, die für dynamische und häufig aktualisierte Informationen geeignet ist (denken Sie an Datenbanken, kollaborative Dokumente usw.).
- Unstrukturierte Daten werden in einer Log-Schicht gespeichert, die Dateneinträge chronologisch anfügt. Diese Schicht ist vergleichbar mit einem Dateisystem, das für große, nur-anhängende Arbeitslasten optimiert ist.
Durch das Stapeln einer KV-Schicht auf der Log-Schicht kann 0G Storage vielfältige Anforderungen von KI-Anwendungen erfüllen – von der Speicherung großer Modellgewichte (unstrukturiert) bis hin zu dynamischen benutzerbasierten Daten oder Echtzeit-Metriken (strukturiert).
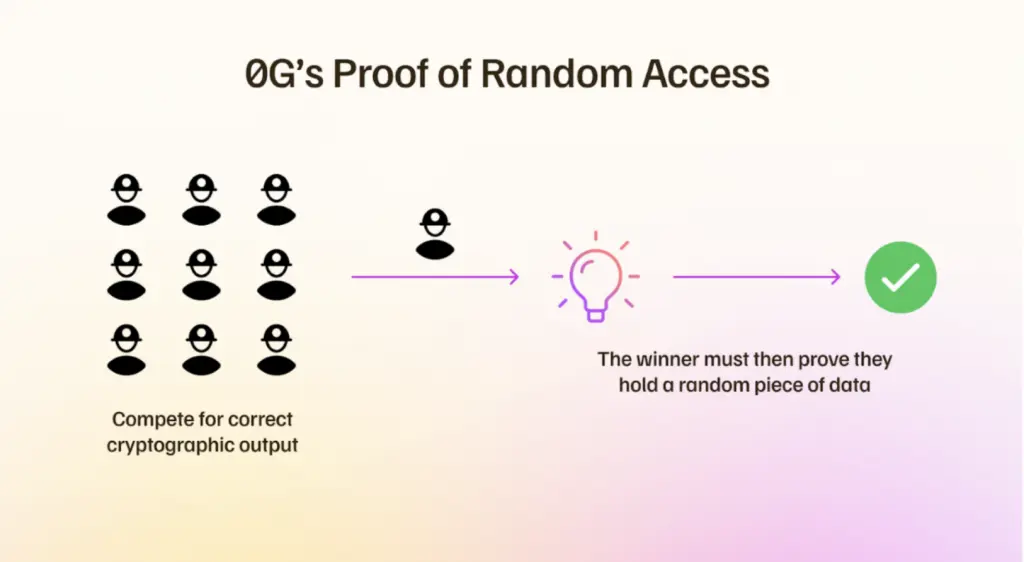
PoRA-Konsens
PoRA (Proof of Random Access) stellt sicher, dass Speicherknoten die Chunks tatsächlich halten, die sie zu speichern behaupten. So funktioniert es:
- Speicher-Miner werden regelmäßig herausgefordert, kryptografische Hashes bestimmter zufälliger Daten-Chunks zu erzeugen, die sie speichern.
- Sie müssen antworten, indem sie einen gültigen Hash (ähnlich einer PoW-ähnlichen Rätsellösung) generieren, der von ihrer lokalen Kopie der Daten abgeleitet ist.
Um gleiche Wettbewerbsbedingungen zu schaffen, begrenzt das System Mining-Wettbewerbe auf 8 TB Segmente. Ein großer Miner kann seine Hardware in mehrere 8 TB Partitionen unterteilen, während kleinere Miner innerhalb einer einzelnen 8 TB Grenze konkurrieren.
Anreizdesign
Daten in 0G Storage werden in 8 GB „Preissegmente“ unterteilt. Jedes Segment hat sowohl einen Spendenpool als auch einen Belohnungspool. Benutzer, die Daten speichern möchten, zahlen eine Gebühr in 0G Token (ZG), die teilweise die Knotenbelohnungen finanziert.
- Basisbelohnung: Wenn ein Speicherknoten gültige PoRA-Beweise einreicht, erhält er sofortige Blockbelohnungen für dieses Segment.
- Laufende Belohnung: Im Laufe der Zeit gibt der Spendenpool einen Teil (derzeit ~4 % pro Jahr) in den Belohnungspool frei, was Knoten dazu anregt, Daten dauerhaft zu speichern. Je weniger Knoten ein bestimmtes Segment speichern, desto größer ist der Anteil, den jeder Knoten verdienen kann.
Benutzer zahlen nur einmal für dauerhaften Speicher, müssen aber eine Spendengebühr über einem Systemminimum festlegen. Je höher die Spende, desto wahrscheinlicher ist es, dass Miner die Daten des Benutzers replizieren.
Lizenzgebührenmechanismus: 0G Storage beinhaltet auch einen „Lizenzgebühren“- oder „Datenfreigabe“-Mechanismus. Frühe Speicheranbieter erstellen „Lizenzgebührenaufzeichnungen“ für jeden Daten-Chunk. Wenn neue Knoten denselben Chunk speichern möchten, kann der ursprüngliche Knoten ihn teilen. Wenn der neue Knoten später die Speicherung (über PoRA) beweist, erhält der ursprüngliche Datenanbieter eine laufende Lizenzgebühr. Je breiter die Daten repliziert werden, desto höher ist die aggregierte Belohnung für frühe Anbieter.
Vergleiche mit Filecoin und Arweave
Ähnlichkeiten:
- Alle drei incentivieren dezentrale Datenspeicherung.
- Sowohl 0G Storage als auch Arweave streben eine permanente Speicherung an.
- Daten-Chunking und Redundanz sind Standardansätze.
Wesentliche Unterschiede:
- Native Integration: 0G Storage ist keine unabhängige Blockchain; es ist direkt in die 0G Chain integriert und unterstützt primär KI-zentrierte Anwendungsfälle.
- Strukturierte Daten: 0G unterstützt KV-basierte strukturierte Daten neben unstrukturierten Daten, was für viele KI-Arbeitslasten, die häufigen Lese- und Schreibzugriff erfordern, entscheidend ist.
- Kosten: 0G beansprucht 10–11 US-Dollar/TB für dauerhaften Speicher, angeblich günstiger als Arweave.
- Leistungsfokus: Speziell entwickelt, um die Durchsatzanforderungen von KI zu erfüllen, während Filecoin oder Arweave eher allgemeine dezentrale Speichernetzwerke sind.
0G DA (Datenverfügbarkeitsschicht)
Datenverfügbarkeit stellt sicher, dass jeder Netzwerkteilnehmer Transaktionsdaten vollständig überprüfen und abrufen kann. Wenn die Daten unvollständig oder zurückgehalten werden, brechen die Vertrauensannahmen der Blockchain zusammen.
Im 0G-System werden Daten gechunked und Off-Chain gespeichert. Das System zeichnet Merkle-Roots für diese Daten-Chunks auf, und DA-Knoten müssen diese Chunks stichprobenartig überprüfen, um sicherzustellen, dass sie mit dem Merkle-Root und den Erasure-Coding-Verpflichtungen übereinstimmen. Erst dann gelten die Daten als „verfügbar“ und werden dem Konsenszustand der Chain hinzugefügt.
DA-Knotenauswahl und Anreize
- DA-Knoten müssen ZG staken, um teilzunehmen.
- Sie werden zufällig über Verifizierbare Zufallsfunktionen (VRFs) in Quoren gruppiert.
- Jeder Knoten validiert nur eine Teilmenge der Daten. Wenn 2/3 eines Quorums die Daten als verfügbar und korrekt bestätigen, signieren sie einen Beweis, der aggregiert und an das 0G-Konsensnetzwerk übermittelt wird.
- Die Belohnungsverteilung erfolgt ebenfalls durch periodische Stichproben. Nur die Knoten, die zufällig ausgewählte Chunks speichern, sind für die Belohnungen dieser Runde berechtigt.
Vergleich mit Celestia und EigenLayer
0G DA greift Ideen von Celestia (Datenverfügbarkeits-Sampling) und EigenLayer (Restaking) auf, zielt aber auf einen höheren Durchsatz ab. Celestias Durchsatz liegt derzeit bei etwa 10 MB/s mit ~12-sekündigen Blockzeiten. EigenDA dient hauptsächlich Layer2-Lösungen und kann komplex in der Implementierung sein. 0G strebt einen Durchsatz von GB/s an, der besser für große KI-Arbeitslasten geeignet ist, die 50–100 GB/s an Datenaufnahme überschreiten können.
0G Compute Netzwerk
Das 0G Compute Netzwerk dient als dezentrale Rechenschicht. Es entwickelt sich in Phasen:
- Phase 1: Fokus auf die Abwicklung für KI-Inferenz.
- Das Netzwerk bringt „KI-Modellkäufer“ (Benutzer) mit Rechenanbietern (Verkäufern) in einem dezentralen Marktplatz zusammen. Anbieter registrieren ihre Dienste und Preise in einem Smart Contract. Benutzer finanzieren den Vertrag vor, nutzen den Dienst, und der Vertrag vermittelt die Zahlung.
- Im Laufe der Zeit hofft das Team, auf vollwertiges KI-Training On-Chain zu expandieren, obwohl dies komplexer ist.
Stapelverarbeitung: Anbieter können Benutzeranfragen stapeln, um den On-Chain-Overhead zu reduzieren, die Effizienz zu verbessern und Kosten zu senken.
0G Chain
Die 0G Chain ist ein Layer1-Netzwerk, das als Grundlage für die modulare Architektur von 0G dient. Sie untermauert:
- 0G Storage (über Smart Contracts)
- 0G DA (Datenverfügbarkeitsbeweise)
- 0G Compute (Abwicklungsmechanismen)
Gemäß den offiziellen Dokumenten ist die 0G Chain EVM-kompatibel, was eine einfache Integration für dApps ermöglicht, die erweiterte Datenspeicherung, -verfügbarkeit oder Rechenleistung benötigen.
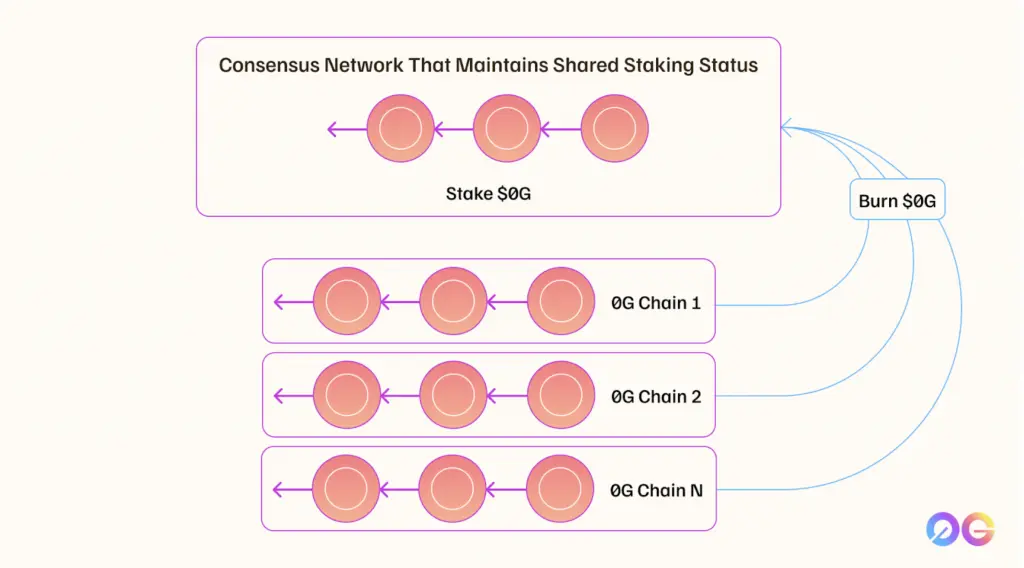
0G Konsensnetzwerk
Der Konsensmechanismus von 0G ist etwas einzigartig. Anstatt einer einzigen monolithischen Konsensschicht können mehrere unabhängige Konsensnetzwerke unter 0G gestartet werden, um verschiedene Arbeitslasten zu bewältigen. Diese Netzwerke teilen dieselbe Staking-Basis:
- Geteiltes Staking: Validatoren staken ZG auf Ethereum. Wenn ein Validator sich fehlverhält, kann sein gestakter ZG auf Ethereum gecuttet werden.
- Skalierbarkeit: Neue Konsensnetzwerke können hochgefahren werden, um horizontal zu skalieren.
Belohnungsmechanismus: Wenn Validatoren Blöcke in der 0G-Umgebung finalisieren, erhalten sie Token. Die Token, die sie auf der 0G Chain verdienen, werden jedoch in der lokalen Umgebung verbrannt, und das Ethereum-basierte Konto des Validators wird mit einem äquivalenten Betrag gemintet, wodurch ein einziger Liquiditäts- und Sicherheitspunkt gewährleistet wird.
0G Token (ZG)
ZG ist ein ERC-20 Token, der das Rückgrat der 0G-Ökonomie darstellt. Er wird über Smart Contracts auf Ethereum gemintet, verbrannt und zirkuliert. In der Praxis:
- Benutzer zahlen für Speicher, Datenverfügbarkeit und Rechenressourcen in ZG.
- Miner und Validatoren verdienen ZG für den Nachweis der Speicherung oder die Validierung von Daten.
- Geteiltes Staking bindet das Sicherheitsmodell an Ethereum zurück.
Zusammenfassung der Schlüsselmodule
Das 0G OS vereint vier Komponenten – Storage, DA, Compute und Chain – zu einem vernetzten, modularen Stack. Das Designziel des Systems ist Skalierbarkeit, wobei jede Schicht horizontal erweiterbar ist. Das Team preist das Potenzial für „unendlichen“ Durchsatz an, was besonders für große KI-Aufgaben entscheidend ist.
0G Ökosystem
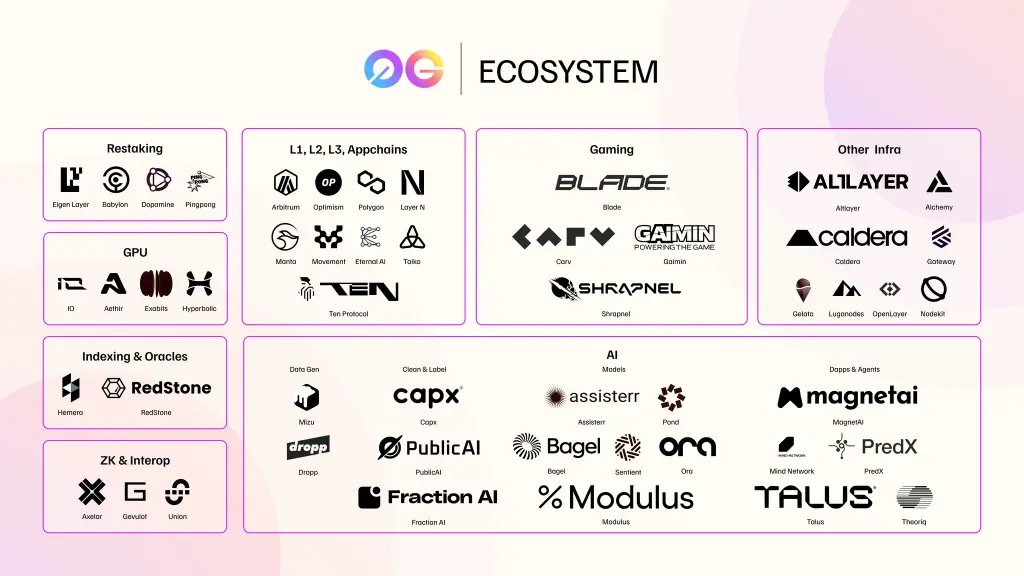
Obwohl relativ neu, umfasst das 0G-Ökosystem bereits wichtige Integrationspartner:
-
Infrastruktur & Tools:
- ZK-Lösungen wie Union, Brevis, Gevulot
- Cross-Chain-Lösungen wie Axelar
- Restaking-Protokolle wie EigenLayer, Babylon, PingPong
- Dezentrale GPU-Anbieter IoNet, exaBits
- Orakel-Lösungen Hemera, Redstone
- Indexierungstools für Ethereum Blob-Daten
-
Projekte, die 0G für Datenspeicherung & DA nutzen:
- Polygon, Optimism (OP), Arbitrum, Manta für L2 / L3 Integration
- Nodekit, AltLayer für Web3-Infrastruktur
- Blade Games, Shrapnel für On-Chain-Gaming
Angebotsseite
ZK- und Cross-Chain-Frameworks verbinden 0G mit externen Netzwerken. Restaking-Lösungen (z. B. EigenLayer, Babylon) stärken die Sicherheit und ziehen möglicherweise Liquidität an. GPU-Netzwerke beschleunigen die Erasure-Codierung. Orakel-Lösungen speisen Off-Chain-Daten oder referenzieren KI-Modellpreise.
Nachfrageseite
KI-Agenten können 0G sowohl für die Datenspeicherung als auch für die Inferenz nutzen. L2s und L3s können 0Gs DA integrieren, um den Durchsatz zu verbessern. Gaming und andere dApps, die robuste Datenlösungen benötigen, können Assets, Logs oder Bewertungssysteme auf 0G speichern. Einige haben bereits mit dem Projekt zusammengearbeitet, was auf eine frühe Ökosystem-Traktion hindeutet.
Roadmap & Risikofaktoren
0G zielt darauf ab, KI zu einem öffentlichen Gut zu machen, das für jeden zugänglich und überprüfbar ist. Das Team strebt einen DA-Durchsatz von GB/s an – entscheidend für Echtzeit-KI-Training, das 50–100 GB/s Datenübertragung erfordern kann.
Mitbegründer & CEO Michael Heinrich hat erklärt, dass das explosive Wachstum der KI eine zeitnahe Iteration entscheidend macht. Das Tempo der KI-Innovation ist schnell; 0Gs eigener Entwicklungsfortschritt muss mithalten.
Potenzielle Kompromisse:
- Die derzeitige Abhängigkeit von geteiltem Staking könnte eine Zwischenlösung sein. Schließlich plant 0G die Einführung einer horizontal skalierbaren Konsensschicht, die inkrementell erweitert werden kann (ähnlich dem Hochfahren neuer AWS-Knoten).
- Marktwettbewerb: Es gibt viele spezialisierte Lösungen für dezentralen Speicher, Datenverfügbarkeit und Rechenleistung. Der All-in-One-Ansatz von 0G muss überzeugend bleiben.
- Akzeptanz & Ökosystemwachstum: Ohne robuste Entwicklerakzeptanz bleibt der versprochene „unbegrenzte Durchsatz“ theoretisch.
- Nachhaltigkeit der Anreize: Die anhaltende Motivation für Knoten hängt von der tatsächlichen Benutzernachfrage und einer gleichgewichtigen Token-Ökonomie ab.
Fazit
0G versucht, dezentralen Speicher, Datenverfügbarkeit und Rechenleistung in einem einzigen „Betriebssystem“ zu vereinen, das On-Chain-KI unterstützt. Durch das Anstreben eines GB/s-Durchsatzes versucht das Team, die Leistungsgrenze zu durchbrechen, die derzeit groß angelegte KI davon abhält, On-Chain zu migrieren. Bei Erfolg könnte 0G die Web3-KI-Welle erheblich beschleunigen, indem es eine skalierbare, integrierte und entwicklerfreundliche Infrastruktur bereitstellt.
Dennoch bleiben viele offene Fragen. Die Machbarkeit des „unendlichen Durchsatzes“ hängt davon ab, ob 0Gs modulare Konsens- und Anreizstrukturen nahtlos skalieren können. Externe Faktoren – Marktnachfrage, Betriebszeit der Knoten, Entwicklerakzeptanz – werden ebenfalls die Beständigkeit von 0G bestimmen. Nichtsdestotrotz ist 0Gs Ansatz zur Bewältigung der Datenengpässe von KI neuartig und ambitioniert und deutet auf ein vielversprechendes neues Paradigma für On-Chain-KI hin.